niversity of Utah Hospitals and Clinics recently affirmed our commitment to pursue Magnet designation. The leaders of our organization have committed to formally support the implementation of the American Nurse’s Credentialing Center’s (ANCC) evidence-based model to guide the development of a culture that empowers nurses across our organization to lead the future of health care change.
The Magnet model is made up of 4 interrelated components and unified with "empirical outcomes." These requirements guide our path to development and sustained nursing excellence.
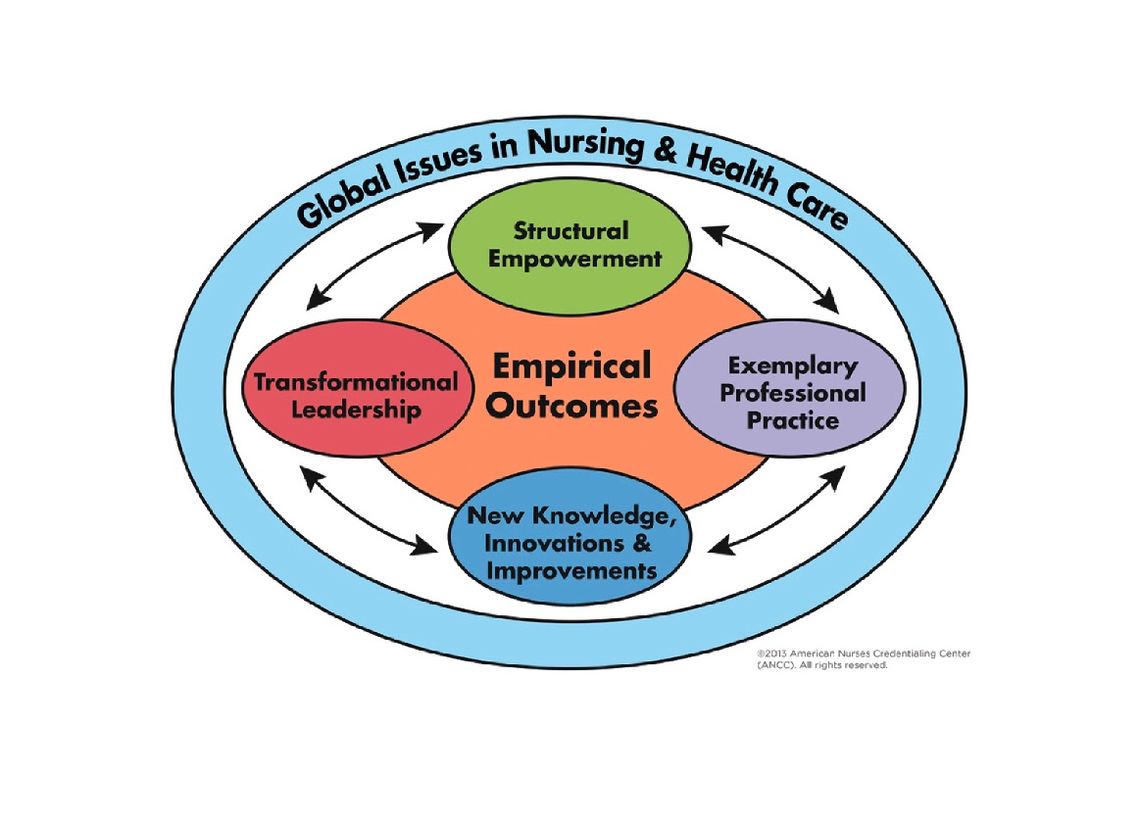
Our nursing excellence journey toward Magnet designation begins with transformational leadership.
What is Transformational Leadership?
Core Elements of Transformational Leadership
Inspirational Motivation: Conveying the vision and purpose in a compelling way that motivates people to reach their full potential to become a proponent and upholder of that vision.
Intellectual Stimulation: Developing foundational structures and processes that spawn creativity and innovation and propel people and organization forward.
Individualized Consideration: Valuing and respecting the perspectives and needs of each individual.
Idealized Influence: Consistently role modelling behaviors that reflect the vision.
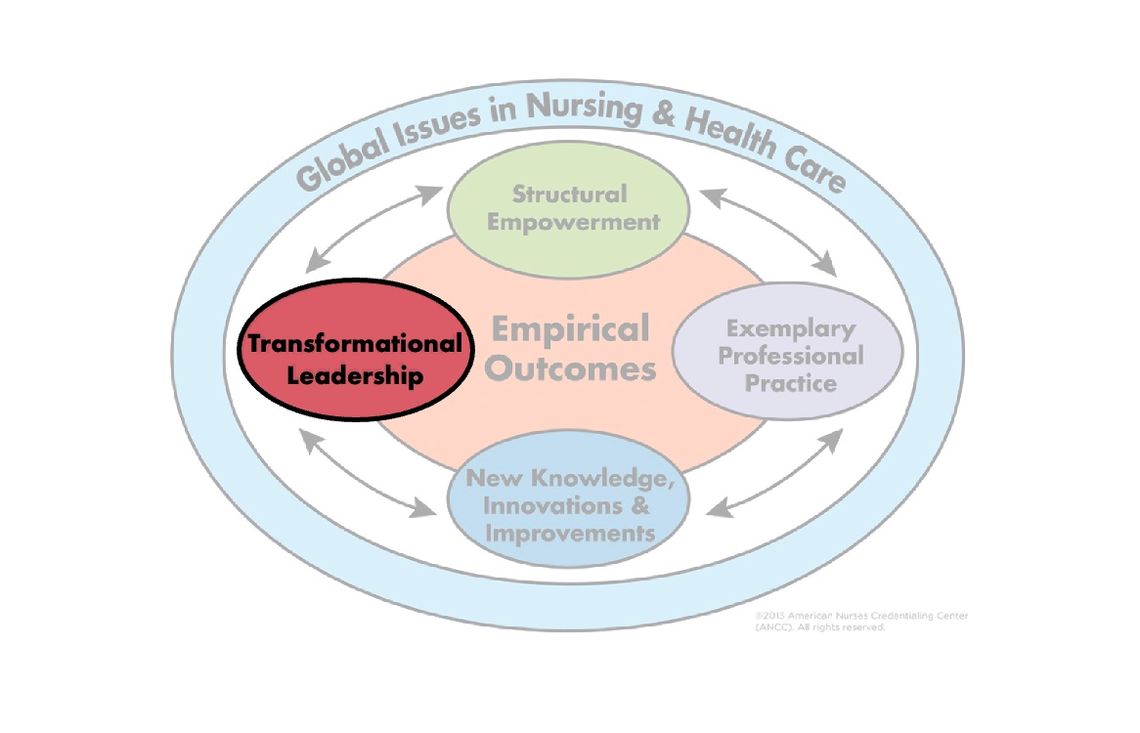
Transformational leaders possess influence, clinical knowledge, and strong expertise in their professional practice. They advocate for their profession at the highest levels within the organization.
First, leaders create a compelling vision to meet the demands of the future that aligns with the larger system. Next, they guide others to realize this course of action through inspiration and influence, role modelling, and by fostering an innovative and brave environment (structures, processes, and culture) to enable achievement. Finally, transformational leaders empower, engage, and inspire others to utilize and enculturate these structures and processes to promote excellence within work environments, clinical care delivery, and patient outcomes.
Our Vision
University of Utah Health created a 5-year strategy, and our 5-year Nursing Strategic Priorities align.
Our FY23 Nursing Tactics outline actionable items for Nursing that proceed in sync with the organization’s priorities. These tactics serve to operationalize our vision and make it bite-sized and achievable.
Inspirational Motivation: Creating the Vision
Vision provides direction. Strategy provides the plan of action. For the first time in its history, the Department of Nursing, under the leadership of Chief Nursing Officer Tracey Nixon, created a vision for nursing excellence and strategy to achieve it. This prospect of a cultural transformation to elevate nursing professional practice stirs excitement for the possibilities and motivates commitment to the cause.
Intellectual stimulation: Developing Foundational Structures and Processes
Our Foundation
Supporting Structures: Professional certification financial reimbursement, RN-BSN program and tuition repayment program, Transition to Practice and Nurse Residency Program, RN Clinical Ladder.
New Structures: Shared Governance, Team Boards and Team Councils, CNO Advisory Board.
Transformational leaders advocate for developing and sustaining innovative structures and processes that promote an exceptional and forward-thinking work environment that yields optimal patient outcomes. They provide foundational support for advocacy, professional development, and interdisciplinary collaboration.
At U of U Health, some of these structures are already established. As we progress on our nursing excellence journey, we’ll take the opportunity to improve these as well as implement new ones.
Individualized Consideration: Inform. Empower. Engage.
It takes the knowledge, abilities and dedication of nurses to create a culture of nursing excellence. All nurses must be given an opportunity to contribute - and understand why they should, and how they can participate. Leaders make the first move by sharing the nursing vision (“the why”), strategic plan, and tactics needed to meet our goals. Next, leaders provide the structure, processes and support so staff are able to impact clinical decision making (“the how”). Finally, leaders encourage interest and involvement from nurses to use their knowledge, skills and ability to influence recommendations and outcomes.
Getting informed
Many of us look to our managers to share information and to keep us updated on changes. Whether a weekly department email update or blog, regular staff meetings or a bulletin board, local leaders engage by informing staff.
The Department of Nursing developed additional methods of communication, such as the Community of Practice newsletter, so that all staff could hear directly from our CNO and other nurse leaders about plans and progress on nursing initiatives.
Empowering teams
Our leaders realized that empowered nurses are necessary to achieve a culture of nursing excellence. Shared governance is a vital element for nurses to use their knowledge and expertise to influence standards of practice, policies and clinical decision-making.
Share Your Voice
Remember that there are ways you can access leadership to be heard.
Engaging all
When teams feel that their voices are heard, respected and impact outcomes, they are more likely to engage in nursing excellence initiatives. Our nursing leaders recognize this. For example, Chief Nursing Officer Tracey Nixon issued a call to action to address rising rates of burnout and staff turnover. A Nursing Health Taskforce with broad departmental representation and strategic systems partnerships launched a 90-day Listen-Sort-Empower (LSE) campaign using in-person and web-based qualitative methods to engage the over 6,000 members of the Department of Nursing to identify upstream drivers of professional burnout. All were invited to participate, and then all were invited to prioritize action steps
Idealized Influence: We are transformational leaders
Throughout the strain of the pandemic and the many lingering post-pandemic challenges, our nursing leaders continue to look ahead to create an optimal workplace environment so that we can provide the very best care for our patients.
The solutions and strategies to address underlying workplace and healthcare issues are not instantaneous and may sometimes even seem counterintuitive. Transformational leaders understand that placing all efforts into immediate stabilization is only a temporary fix and that cultural transformation takes time and can often be turbulent.
It’s our priority to create a culture that is innovative, courageous, nimble, and ready to morph into not only what is needed at the moment but also to support the vision for our future. Our nursing leaders strive to approach change purposefully and proactively. They must have the courage to initiate controlled destabilization, knowing that this path will allow us to reach our vision, cultivate a culture of excellence and yield optimal patient outcomes. Together, we are creating an empowered, collaborative and innovative environment. There’s durability in that.
Our transformational leaders have been diligently preparing for our nursing excellence journey. They convey our vision and consistently model behaviors that support it. As our work continues to progress, the attitudes and beliefs that support a culture of nursing excellence take root in the organization, branch out, and positively influence others. Leaders grow new leaders at every level and in every role in our organization. Where are the transformational leaders? Look around you…they are closer than you think.
This article originally posted February 17, 2023. It was updated by the contributor on November 27, 2023 to reflect current information.
Mary-Jean (Gigi) Austria
Magnet Program Director Gigi Austria introduces our new approach to achieving nursing excellence at University of Utah Health.
The Department of Nursing’s Patient Care Excellence Council proudly introduces our new professional practice model. This model reflects the core values and beliefs of our nursing community, guiding their daily decisions and practices. Join us as we share the multi-year journey that brought this model to life.
The Shared Governance Support Team has developed a list of resources for new shared governance leaders to equip them to lead and guide team members in engaging in shared decision-making at the local level.